Building Science - Energy Efficient Uncomfortable Buildings
The separation between the internal space and the external environment is for the following reasons
- control heat flow
- control air flow
- control water vapour flow
- control rain
- control ground water
- control light and solar radiation
- control noise and vibration
- control contaminant, environmental hazards and odour
- control insects, rodents and vermin
- control fire
- provide strength and rigidity
- be durable
- be aesthetically pleasing
- be economical
Arrhenius Equation
For every 10 degree K rise reaction rate doubles
k is the rate constant (frequency of collisions resulting in a reaction),
T is the absolute temperature (in kelvins),
A is the pre-exponential factor, a constant for each chemical reaction,
Ea is the activation energy for the reaction (in the same units as RT),
R is the universal gas constant.
Damage functions
- water
- heat
- UV radiation
Second law of thermodynamics
- heat flow from warm to cold
- moisture flow from warm to cold
- moisture flow from more to less
- air flow from high pressure to low pressure
- gravity acts down
Thermal gradient – thermal diffusion
Concentration gradient – molecular diffusion
Vapour diffusion
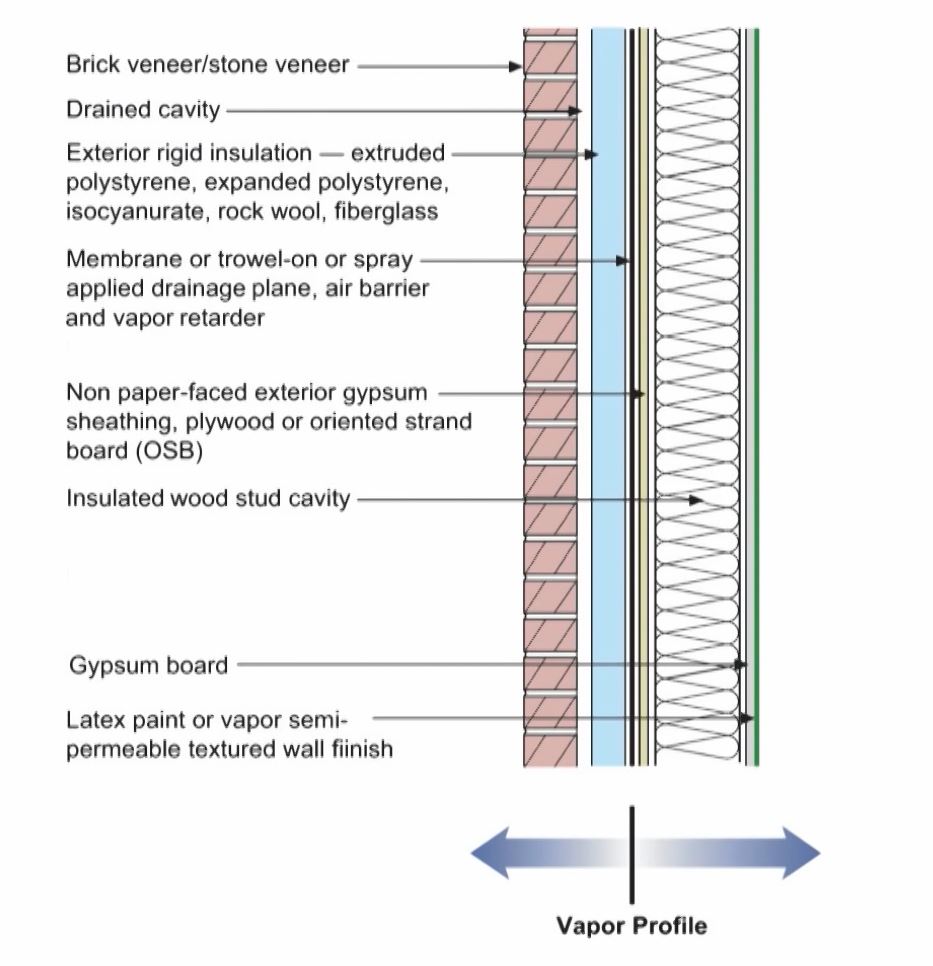
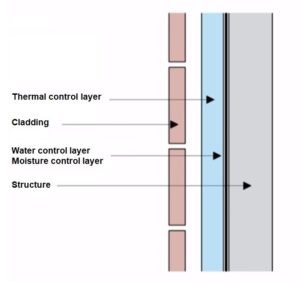
Control mechanism in order of importance
- water control layer
- air control layer
- vapour control layer
- thermal control layer
You can never proof science, you can only disprove science. Science is never settled!
Why condensation occur on vapour barrier

To prevent condensation on the vapour barrier, there should not be any vapour barrier on the wall to prevent condensation on the wall insulation.
Note: Don’t use open cell spray foam in cold climate, use closed cell.
The perfect wall commercial.
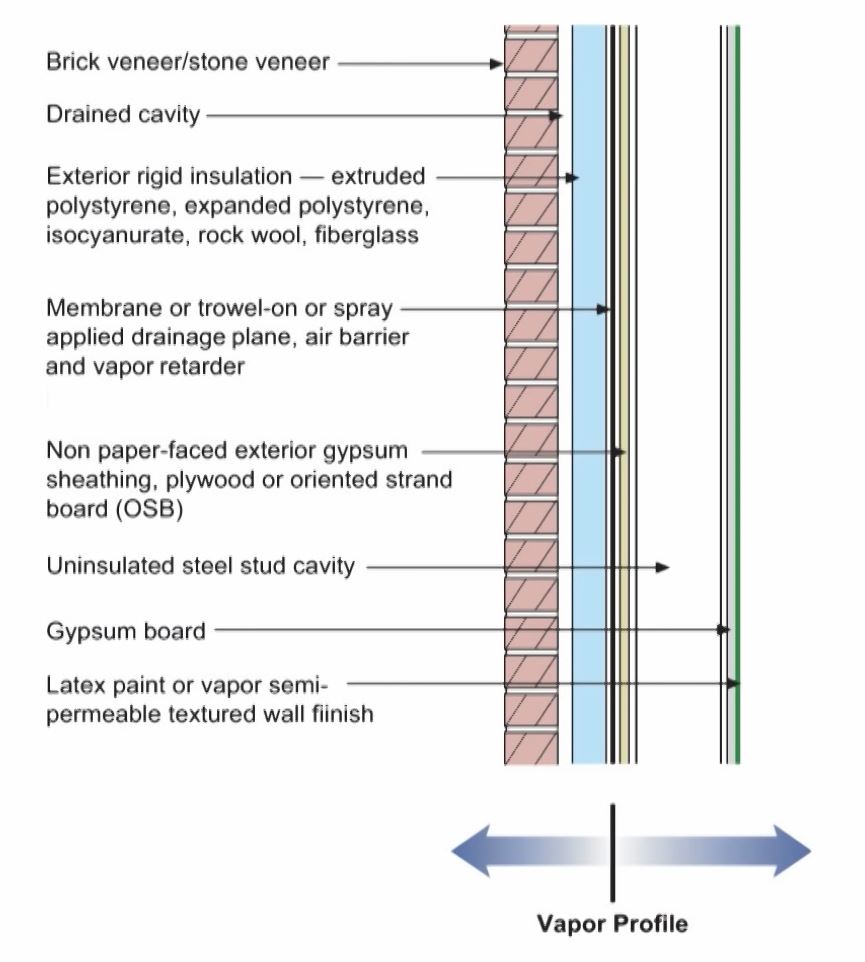
The perfect wall residential with timber frames