Diminishing effect of insulation thickness or R-value
Diminishing effect of insulation thickness
or R-value
Does it mean that when we double the insulation thickness, we would have reduced the heat transfer by half? How thick should the insulation be? Before we look into the diminishing effect of insulation thickness, we need to understand the key concept behind heat transfer.
Heat transfer is given by this formula below
Heat transfer is given by this formula below
where
Q is the heat transfer in W
U is the heat transfer coefficient in W/(m²K)
A is the area in m²
T is the temperature difference in Kelvin
and we also know that
Q is the heat transfer in W
U is the heat transfer coefficient in W/(m²K)
A is the area in m²
T is the temperature difference in Kelvin
and we also know that
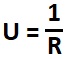
R is the thermal resistance in (m²K)/W
therefore
therefore
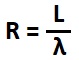
and R-value is a function of thickness by the formula below
L is the thickness of the material in metres and
λ is the thermal conductivity in W/mK.
Using hypothetical figures below Area = 100m²
Temperature difference = 15K and above mentioned formula for heat transfer, we are able to calculate heat transfer at different R-value as tabulated in the table below
λ is the thermal conductivity in W/mK.
Using hypothetical figures below Area = 100m²
Temperature difference = 15K and above mentioned formula for heat transfer, we are able to calculate heat transfer at different R-value as tabulated in the table below

Insulation thickness with R-value above 4 (m²K)/W, gives very little additional return on your investment, more so for ductwork insulations at R3 at max. I don’t see the R-value stated in the BCA/ NCC be increased in the near future.
Related
Read more: Fan wall
Read more: How to verify the percentage of outside air in an enclosure
Read more: BCA Part J5 Air-conditioning system control
Read more: Microbial Induced Corrosion (MIC) in Pipes
Read more: Is your kitchen exhaust system a fire hazard
Read more: Lesson Learnt – Fan troubleshooting
Read more: What is coanda effect
Read more: What do you want from your BMS